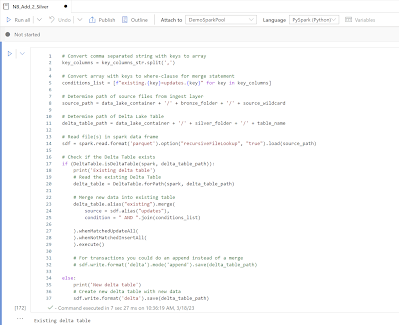
CaseSince the introduction of ChatGPT in late 2022, people have started to discover the various applications of Large Language Models (LLMs) in coding and beyond. LLM’s can be a helpful sparring partner in developing and reviewing code. As an IT consultant, I've started using LLMs in my coding practices. This made me wonder: ‘Can I automate the use of LLM in my development process?’. Which is Azure Synapse in my case.
And the short answer is: ‘yes, you can’
Solution
This blog serves as a step-by-step guide to integrating GPT 3.5 into your Azure DevOps pipeline for automated code reviews. The solution that I’m proposing checks which files have changed between the source branch and the target branch in a pull request. If one of these changed files is a Synapse notebook, the code is passed on the GPT model on your tenant with the request to provide feedback. The feedback given by the GPT model is posted as a comment in the pull request.
Before you start, make sure you have the following three resources set up and configured correctly. I’ll include links to other step-by-step guides to create the required resources.
Required resources:
- Azure Synapse Workspace
- Azure DevOps Project (including a repository linked to the Synapse Workspace)
- Access to the Microsoft Azure OpenAI service*
*Access to the Microsoft Azure OpenAI service is limited at the time of writing.
1) Create a GPT model in Azure OpenAI serviceOnce you have gained access to the Azure OpenAI service you need to create an OpenAI service and deploy a model. Click here to follow the comprehensive guide by Christopher Tearpak on creating and deploying your GPT model in Azure. The result should be an OpenAI service resource:
 |
| Expected result after creating your own OpenAI Service |
With a GPT model deployment:
 |
| Expected result after deploying your own GPT model |
2) Setup and configure Azure DevOpsScripts
Three scripts must be present in your repository. These scripts can be found at the SynapseBuildValidations repository (which also contains other useful build validation scripts).
Download the scripts from the SynapseBuildValidations repository. Here is what each script does:
- get_GPT_feedback.py: Retrieves and passes your code to GPT and posts the feedback to the pull request.
- requirements.txt: Lists the required Python packages for the above script.
- GPT_code_review.yml: Contains the pipeline configuration.
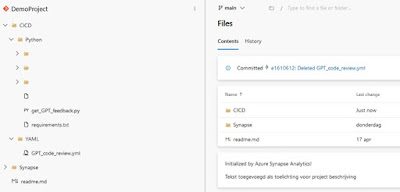 |
| Expected folder/file structure for your repository |
Create variable group
Create a new library under “Pipelines” and give it the name: “GPT_connection_data”.
Add the following variables:
- openai_api_base
- openai_api_key
- openai_api_type
- openai_api_version
- synapse_root_folder
The variables openai_api_base and openai_api_key can be found in the “Keys and Endpoint” tab in your OpenAI resource.
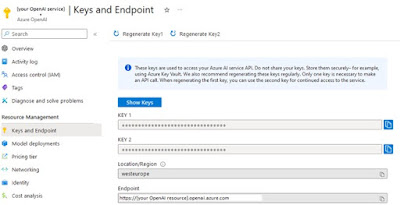 |
| Find your Key and Endpoint in "Keys and Endpoint" of your OpenAI service |
Copy the “Endpoint” to “Openai_api_base” and one of the keys to “openai_api_key”.
Openai_api_type needs to be filled with: “azure” and openai_api_version “2023-03-15-preview”.
The variable synapse_root_folder contains the path to the root folder containing the synapse files. In my case it’s just “Synapse”, because all the synapse files can be found in {repository_root}/Synapse
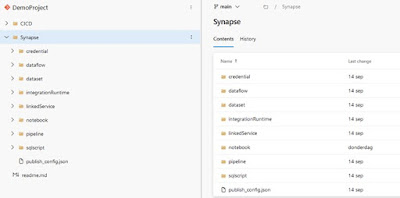 |
| An example of my repository, where the synapse_root_folder is "Synapse" |
After
you’ve set all your variables, the resulting variable group should look like
this:
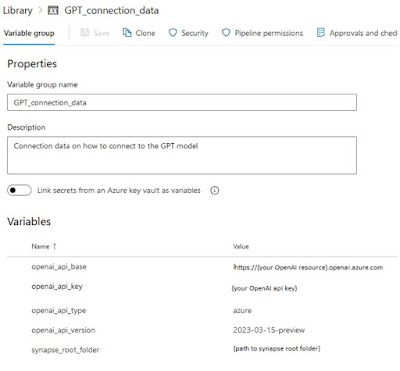 |
| Expected variable group in Azure DevOps |
Create a pipeline
The GPT_code_review.yml contains the pipeline code needed to configure the agent and execute the get_GPT_feedback.py script. You need to create a new pipeline based on the GTP_code_review.yml.
Click
here to follow the comprehensive guide by Xeladu on creating a pipeline.
The result should be as follows:
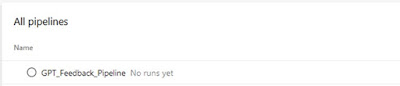 |
| The resulting pipeline after following the guide |
Disable “Override YAML continuous integration (CI) trigger”
Now you’ll need to disable the CI trigger of your new pipeline.
Open the pipeline in edit mode, select the three vertical dots and select “Trigger”
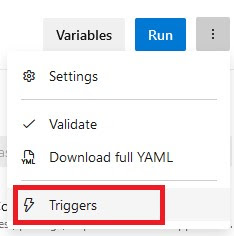 |
| Select triggers to change the trigger settings |
Then select your project under “Continuous integration”, check “Override the YAML CI trigger”, check disable CI and select “save”.
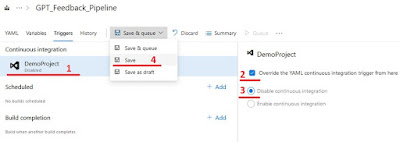 |
| Steps to disable the CI trigger |
Permit pipeline access to variable group resourceAfter you’ve disabled the CI trigger, you’ll need to start a run. During the run you’ll get a notification that the pipeline needs permission to access a resource. Click on the “View” button and permit the access to the variable group GPT_connection_data by clicking the “Permit” button. The run will continue and eventually fail.
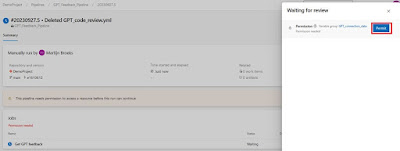 |
| Permit the pipeline to access the variable group |
Note that this pipeline is designed to operate only within the context of a pull request. Because it’s dependent on a few system variables that are only present on the build agent during a pull request.
Set rights for build agent
The GPT feedback is posted in comments of the pull request. The build agent needs to have the right to post in the pull request. Go to “Project settings” and select “Repositories”, when you’re in “Repositories” select security and select your “{Projectname} Build Service“.
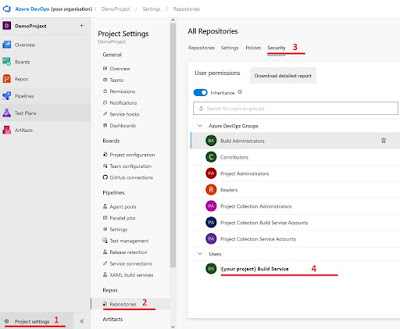 |
| Steps to select the build service user |
Once the build service user is selected, you must grant this user permission to contribute to pull requests.
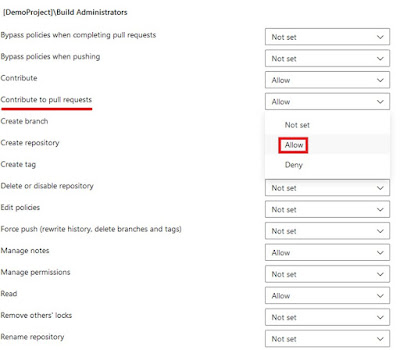 |
| Set the "Contribute to pull request" to Allow |
After these actions, your build agent user has access to write comments to a pull request.
Add the pipeline as build validationThe final step is adding your GPT_Feedback_pipeline as build validation on your desired branch. Go to “Project settings”, select “Repositories” and select the repository where you want to add the pipeline (“DemoProject” in my example). With the repository select “Policies”
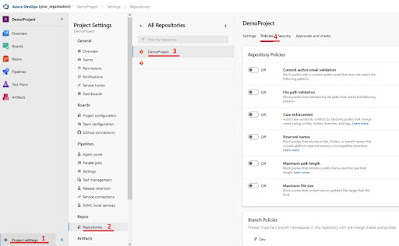 |
| Steps to get to the branch you want to set the build validation to |
Select the branch where you want to have the build validation.
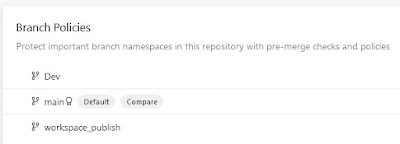 |
| Select the branch you want to set the build validation to |
Within this branch, select the plus icon in the build validation component.
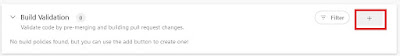 |
| Select the plus to add a pipeline as build validation |
In the “Add build policy” pop-up, select the build pipeline: “GPT_Feedback_Pipeline”, set a display name and select “Save”
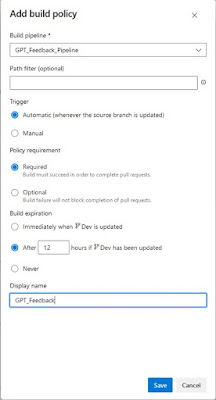 |
Pop-up to select a pipeline
as build validation |
Now you’re good to go! When you merge another branch into the branch on which you have enabled the branch validation the GPT_Feedback_pipeline will run.
3) Testing
Now its time to perform a pull request. You will see that the validation will first be queued. So this extra validation will take a little extra time, especially when you have a busy agent. The pipeline should always run without errors. When there is no feedback, there won’t be any comments. This means that your code is perfect :) or there aren’t any changes to any of the notebooks. However, when there is feedback, it will be posted in the comments.
Let’s see de build pipeline in action. First off, we need a new branch, in my case a feature branch
- Create a new branch in Synapse called Feature
- Create a new notebook
- Create some sample code in python or SQL
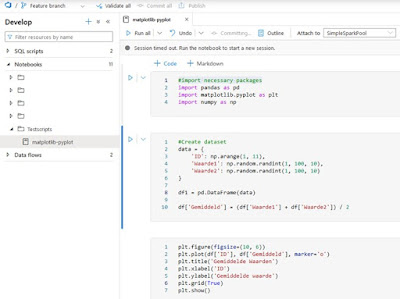 |
| Sample code in Azure Synapse |
- Create a pull request based on your new branch
- Fill out the details of your pull request and make sure you’re merging into the branch with the GPT build validation
- Confirm the creation of your pull request.
- Your pull request is created and the GPT_Feedback pipeline starts running
- After the pipeline has run successfully and the GPT model gave feedback for improvement. The feedback is posted in the comments of the merge request
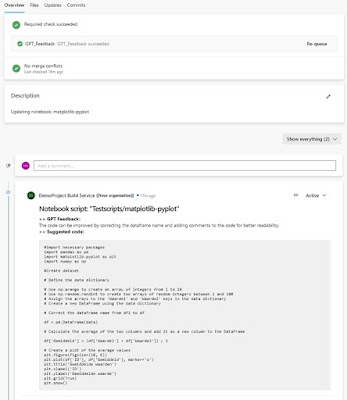 |
| GPT response in the comments of your pull request |
4) Altering the feedback to your situation
The prompt sent to the GPT model is pre-determined and might not suit your specific situation. At the time of writing, the prompt is included in the get_GPT_feedback.py script. This script contains a get_gpt_response function. The first lines of this function are used to set three strings. These strings contain the prompt for the “system”, “user” and “assistant” roles passed to the GPT model. More on the use of these roles can be found
here. To alter the prompts passed to the GPT model, you need to alter the strings: content_system_string, content_assistant_string and/or content_user_string.
 |
| Subset of the get_GPT_feedback.py where the GPT commands are set |
Conclusion
In this post you learned how to integrate GPT into your deployment pipeline. Your pipeline will provide feedback on your changed of added synapse notebooks. The feedback is posted as comments in the pull request in Azure DevOps. You can customize the prompt to suit your specific needs.